N Cholangitis 3j3y4a
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report l4457
Overview 6h3y3j
& View N Cholangitis as PDF for free.
More details h6z72
- Words: 560
- Pages: 4
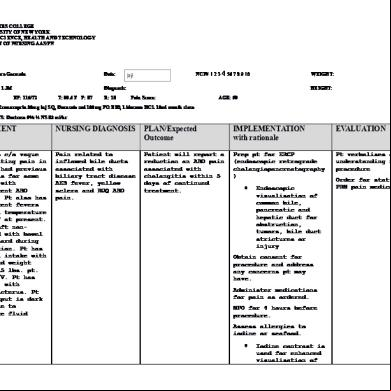
NURSING CARE PLAN CUES
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Subjective: The patient verbalized: “Masakit tiyan ko”
Acute pain related to spasms and abdominal pain.
Objective Observed evidence of pain Guarding behavior Frequently changing position to avoid pain Irritability Facial grimace
ANALYSIS
GOAL & OBJECTIVES
Cholangitis is the most serious complicatio n of gallstones and more difficult to diagnose. It is caused by impacted stone in the common bowel duct, resulting in bile stasis, bacteremia and septicemia if left untreated. It is more ikely to occur when an already infected
Goal: After 3 hours of nursing interventions the client will be free from experiencing pain in the abdomen.
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
__Met __Partially met __Unmet
Objectives: 1. After 40 minutes of assessment, the client will be able to describe the characteristic, onset, location, duration, severity, and precipitating factors of pain.
EVALUATION
>Assess the client of pain to include the characteristic, onset, location, duration, severity, and precipitating factors of pain.
2. After 15 minutes >Assess for the of assessing for presence of fear or the presence of anxiety. fear or anxiety, the client will be able to verbalize if she’s feeling
>Pain is a subjective experience and must be described by the patient in order to plan effective treatment. (http://wps.prenhall. com/wps/media/obje cts/3918/4012970/N ursingTools/ch46_NC P_AcutePain)
>Fear and anxiety can alleviate client’s perception of pain. (http://bja.oxfordjour nals.org/content/87/ 1/144.full)
bile duct becomes obstructed. Patients having cholangitis is suffering from severe abdominal pain.
anxious.
3. After 15 minutes >Assess causes of of assessing for possible discomfort. client’s discomfort, client will verbalize the cause of discomort.
(All-in-one Care Planning Resource by Swearinge n; page 453)
> Discomfort can be caused or aggravated by presence of nonpatent indwelling catheters causing bladder pain, NG tube resulting in gastric fluid and gas accumulation, or parenteral lines that have infiltrated IV fluids or medications. (Nursing Care Plans by Doenges, 8th ed; page 798)
4. After 10 minutes of monitoring the patient for pain, the client will be able to verbalize the rate of pain she is experiencing.
>Monitor patient for pain or other discomfort. Devise a pain scale with patient, rating discomfort on a scale of 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst pain)
5. After 30 minutes > Encourage use of of deep breathing relaxation techniques
>Enables more precise measurement of discomfort and relief obtained. (All-in-one Care Planning Resource by Swearingen; page 454)
> Relieves muscle and emotional
exercise and doing the bent-knee position, the client will be able to verbalize that the abdominal tension will be relieved/reduced.
such as deepbreathing exercises.
tension; enhances sense of control and may improve coping abilities.
>Position the client in a bent-knee position.
>This position decreases tension on abdominal contents to promote comfort. (All-in-one Care Planning Resource by Swearingen; page 454)
6. 30 minutes after >ister istering analgesics as analgesics, client prescribed. will report reduced abdominal pain.
>Nonsteroidal antiinflammantory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioid analgesics may be indicated, depending on severity of the pain. For the postoperative patient, continuous IV of opioid analgesics are used with increasing frequency and efficacy. (All-in-one Care
Planning Resource by Swearingen; page 455)
7. After 40 minutes of nursing interventions the client will be able to verbalize willingness to alleviate pain.
> Note client’s attitude towards pain and use of pain medications. > Evaluate client’s response to analgesics and assist in transitioning or altering drug regimen, based on individual needs and protocols.
>To promote wellness
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Subjective: The patient verbalized: “Masakit tiyan ko”
Acute pain related to spasms and abdominal pain.
Objective Observed evidence of pain Guarding behavior Frequently changing position to avoid pain Irritability Facial grimace
ANALYSIS
GOAL & OBJECTIVES
Cholangitis is the most serious complicatio n of gallstones and more difficult to diagnose. It is caused by impacted stone in the common bowel duct, resulting in bile stasis, bacteremia and septicemia if left untreated. It is more ikely to occur when an already infected
Goal: After 3 hours of nursing interventions the client will be free from experiencing pain in the abdomen.
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
__Met __Partially met __Unmet
Objectives: 1. After 40 minutes of assessment, the client will be able to describe the characteristic, onset, location, duration, severity, and precipitating factors of pain.
EVALUATION
>Assess the client of pain to include the characteristic, onset, location, duration, severity, and precipitating factors of pain.
2. After 15 minutes >Assess for the of assessing for presence of fear or the presence of anxiety. fear or anxiety, the client will be able to verbalize if she’s feeling
>Pain is a subjective experience and must be described by the patient in order to plan effective treatment. (http://wps.prenhall. com/wps/media/obje cts/3918/4012970/N ursingTools/ch46_NC P_AcutePain)
>Fear and anxiety can alleviate client’s perception of pain. (http://bja.oxfordjour nals.org/content/87/ 1/144.full)
bile duct becomes obstructed. Patients having cholangitis is suffering from severe abdominal pain.
anxious.
3. After 15 minutes >Assess causes of of assessing for possible discomfort. client’s discomfort, client will verbalize the cause of discomort.
(All-in-one Care Planning Resource by Swearinge n; page 453)
> Discomfort can be caused or aggravated by presence of nonpatent indwelling catheters causing bladder pain, NG tube resulting in gastric fluid and gas accumulation, or parenteral lines that have infiltrated IV fluids or medications. (Nursing Care Plans by Doenges, 8th ed; page 798)
4. After 10 minutes of monitoring the patient for pain, the client will be able to verbalize the rate of pain she is experiencing.
>Monitor patient for pain or other discomfort. Devise a pain scale with patient, rating discomfort on a scale of 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst pain)
5. After 30 minutes > Encourage use of of deep breathing relaxation techniques
>Enables more precise measurement of discomfort and relief obtained. (All-in-one Care Planning Resource by Swearingen; page 454)
> Relieves muscle and emotional
exercise and doing the bent-knee position, the client will be able to verbalize that the abdominal tension will be relieved/reduced.
such as deepbreathing exercises.
tension; enhances sense of control and may improve coping abilities.
>Position the client in a bent-knee position.
>This position decreases tension on abdominal contents to promote comfort. (All-in-one Care Planning Resource by Swearingen; page 454)
6. 30 minutes after >ister istering analgesics as analgesics, client prescribed. will report reduced abdominal pain.
>Nonsteroidal antiinflammantory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioid analgesics may be indicated, depending on severity of the pain. For the postoperative patient, continuous IV of opioid analgesics are used with increasing frequency and efficacy. (All-in-one Care
Planning Resource by Swearingen; page 455)
7. After 40 minutes of nursing interventions the client will be able to verbalize willingness to alleviate pain.
> Note client’s attitude towards pain and use of pain medications. > Evaluate client’s response to analgesics and assist in transitioning or altering drug regimen, based on individual needs and protocols.
>To promote wellness