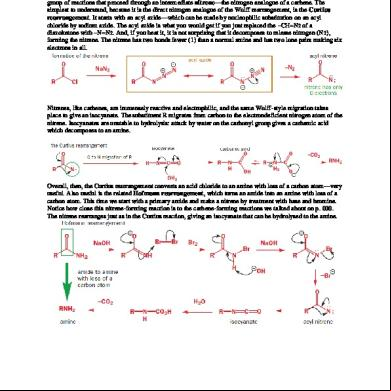
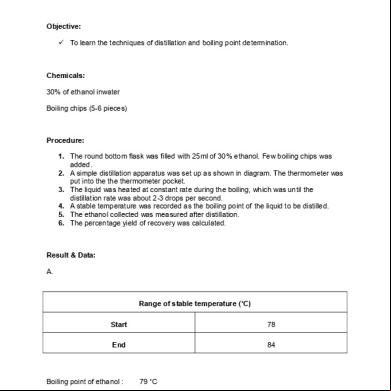
Experiment 5 Chm207 Intermediate Organic Chemistry Reactions Of Aliphatic Alcohols And Phenol 5o5v4z
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report l4457
Overview 6h3y3j
& View Experiment 5 Chm207 Intermediate Organic Chemistry Reactions Of Aliphatic Alcohols And Phenol as PDF for free.
More details h6z72
- Words: 1,112
- Pages: 5
Experiment 5: Reactions of Aliphatic Alcohols and Phenol
Objective: To investigate the reaction of aliphatic alcohols and phenols.
Chemicals: Each of the chemicals in (i) to (v) required around 10ml i ii iii iv v
Ethanol Butanol Butan-2-ol 2-methylpropan-2-ol Phenol Sodium carbonate solution Sodium metal Ethanoic acid/acetic acid Concentrated H2SO4 Dilute H2SO4 Acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) Lucas reagent Sodium hydroxide solution 2.0 M Bromine water Iron (III) chloride Iodine solution A bottle of disttiled water
Appratus: 10 test tubes, test tube rack, water bath, evaporating dish, stopper, wooden splints and litmus paper or pH paper.
Results and data: Observations Test Ethanol
Phenol
A) Solubility
A) Acidity A) Addition
of
Na2CO3
The solution mixture became
The solution mixture form two
homogenous mixture.
layer.
The solution is acidic. It turns
The solution is acidic. It turns
litmus paper from blue to red.
litmus paper from blue to red.
2 drops of Na2CO3 turns litmus
2 drops of Na2CO3 turns litmus
paper from red to blue.
paper from red to blue.
A gas B) Reaction
with
sodium metal
C) Esterification
Test D) i ii iii iv E) i ii iii
2-ol phenol Lucas test Butanol Butan-2-ol 2-methylpropan-
A gas
was
produced
(white
smoke). It produced a pop sound
smoke). It produced a loud pop
when test with burning wooden
sound when test with burning
splint.
wooden splint.
Smooth or weak pungent smell
Smooth or weak pungent smell
was produced.
was produced.
i. ii.
The solution turned from orange yellowish to dark brown Two layers were formed. Top layer is cloudy brown and bottom
iii. iv.
layer is light brown. No changes occur. Only gas bubble were produced The solution turn from black oily to dark brown with precipitate.
i. ii. iii.
The solution remains unchanged. The solution turns from clear orange to milky solution. The solution forms two layers. Top layer is clear and bottom
i. on
methyl alcohols) i Butanol ii Butan-2-ol iii 2-methylpropan-
The solution turns from cloudy white to clear white solution. The reaction is very slow.
ii.
The solution turns from red precipitate to cloudy white. The
iii.
reaction is at normal rate. The solution turns into clear yellow. The reaction is very fast.
on
the aromatic ring Phenol and addition
of
bromine
water
drop.
(white
layer is cloudy yellow.
2-ol F) Iodoform
2-ol G) Substitution
produced
Observation
Oxidation Ethanol Butan-2-ol 2-methylpropan-
(reaction
was
i.
The solution turns into white solution. When bromine was added, two layers were form. Top layer is cloudy while the bottom layer is clear.
H) Test group Neutral
on Fe
enol (III)
chloride solution
i
The solution turns from colourless to dark blue.
into an aqueous phenol
Questions/Discussions: 1. Select ONE compound from the following pairs of compounds which is more water soluble. Explain your answer. a) Ethanol and hexanol Ans: Ethanol is more soluble in water. Hexanol is not soluble in water. Ethanol consists of two carbon atoms with a single bond between them. So it is easier for a short hydrocarbon chain to bond with water molecules compared to hexanol which is a long hydrocarbon chain. b) Propanol and 1,2,3-propanetriol Ans:
Propanol is more soluble in water. Propanol is an alcohol and polar, and exhibits hydrogen bonding compared to 1,2,3-propanetriol. Water is polar and exhibits hydrogen bonding. The polar natures of the alcohol and water allow the alcohol to be completely miscible in water. 2. Suggest a chemical test(s) to distinguish the following pairs of compounds. Include the reagents, reaction conditions and observations. Write the equation involved. a) 2-butanol and 3-pentanol Ans: To distinguish between 2-butanol and 3-pentanol, solubility test is needed. 2-butanol is easier to bond with water molecule compared to 3-pentanol due to the short hydrocarbon chain of 2-butanol. Reagent: Sodium carbonate solution Reaction condition: Room temperature Observation: 2-butanol form homogenous mixture while 3-pentanol form 2 layer of solution. Equation: R-OH + Na R-O-Na+ + ½ H2 b) Phenol and phenylethanol Ans: To distinguish between phenol and phenylethanol, esterification test is required. Phenol does not form ester by direct reaction with carboxylic acid compared to phenylethanol. Reagent: Carboxylic acid Reaction condition: Room temperature Observation: Phenylethanol form ester directly from the reaction with carboxylic acid. Equation: C6H5OH + R-COOH No reaction c) Phenol and methylphenol Ans: To distinguish between phenol and methylphenol,iodoform test is needed. Methylphenol react quickly with iodine compared to phenol. Reagent: Iodine solution Reaction condition: Room condition Observation: Methylphenol when react with the reagent does not form precipitate. Equation: CH3C6H4OH + 3I- CH3C6HI3OH + 3I 3. Explain the following observations. a) Ethanol is less acidic than phenol. Ans: Phenol is more acidic than ethanol because of the presence of double bond in it. Phenol can remove its hydrogen to make it more stable. Electron density on oxygen atom decreases in comparison to oxygen atom present in alcohols, so phenol can less donate than alcohol. According to Lewis concept of acid and base, which can donate more is more basic and less is acidic.
b) Both phenol and methanol reacts with sodium but only phenol dissolves in aqueous NaOH. Ans: The reason why phenol is more soluble in NaOH than in water is because phenol is slightly acidic. By mixing with NaOH, it causes the phenol to release the H+ to form sodium phenoxide. the reaction between NaOH and phenol is exothermic, and the equilibrium lies far to the right. This makes the sodium phenoxide extra stable. c) 2-methylpropanol does not give yellow precipitate with iodine in NaOH. Ans: A visible precipitate of this compound will form from a sample only when either a methyl ketone, ethanal, ethanol, or a methyl secondary alcohol is present. 2methylpropanol is an primary alcohol, so it does not form precipitate.
d) 1-methylcyclopentanol does not change the purple colour of KMnO4/H+ , ∆ Ans: KMnO4 is pink in a solution without oxidizing reagents. Adding ethanol should change it to a brown solution. If adding ethanol can not change the solution to brown, then its environment is already acidic and will not reduce.
Conclusion: Hydroxyl group are connected to an alkyl carbon are called alcohols. They can be classified into primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols depend on the number of carbon atoms bonded to the carbon with the hydroxyl group. In hydroxyl group, they are alcohol and phenol. This two compound can be distinguish by several tests such as oxdation, solubilty, esterification, Lucas test, iodoform, substitution and test on enol group. Some test produced the same product and reaction while some are not. In conclusion, the reaction of aliphatic alcohols and phenol were investigated.
References: 1. John McMurry, Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry (5th Edition), 2003, pg. 106-126 2. G.L. Patrick, Organic Chemistry, (2nd Edition), 2004.
Objective: To investigate the reaction of aliphatic alcohols and phenols.
Chemicals: Each of the chemicals in (i) to (v) required around 10ml i ii iii iv v
Ethanol Butanol Butan-2-ol 2-methylpropan-2-ol Phenol Sodium carbonate solution Sodium metal Ethanoic acid/acetic acid Concentrated H2SO4 Dilute H2SO4 Acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) Lucas reagent Sodium hydroxide solution 2.0 M Bromine water Iron (III) chloride Iodine solution A bottle of disttiled water
Appratus: 10 test tubes, test tube rack, water bath, evaporating dish, stopper, wooden splints and litmus paper or pH paper.
Results and data: Observations Test Ethanol
Phenol
A) Solubility
A) Acidity A) Addition
of
Na2CO3
The solution mixture became
The solution mixture form two
homogenous mixture.
layer.
The solution is acidic. It turns
The solution is acidic. It turns
litmus paper from blue to red.
litmus paper from blue to red.
2 drops of Na2CO3 turns litmus
2 drops of Na2CO3 turns litmus
paper from red to blue.
paper from red to blue.
A gas B) Reaction
with
sodium metal
C) Esterification
Test D) i ii iii iv E) i ii iii
2-ol phenol Lucas test Butanol Butan-2-ol 2-methylpropan-
A gas
was
produced
(white
smoke). It produced a pop sound
smoke). It produced a loud pop
when test with burning wooden
sound when test with burning
splint.
wooden splint.
Smooth or weak pungent smell
Smooth or weak pungent smell
was produced.
was produced.
i. ii.
The solution turned from orange yellowish to dark brown Two layers were formed. Top layer is cloudy brown and bottom
iii. iv.
layer is light brown. No changes occur. Only gas bubble were produced The solution turn from black oily to dark brown with precipitate.
i. ii. iii.
The solution remains unchanged. The solution turns from clear orange to milky solution. The solution forms two layers. Top layer is clear and bottom
i. on
methyl alcohols) i Butanol ii Butan-2-ol iii 2-methylpropan-
The solution turns from cloudy white to clear white solution. The reaction is very slow.
ii.
The solution turns from red precipitate to cloudy white. The
iii.
reaction is at normal rate. The solution turns into clear yellow. The reaction is very fast.
on
the aromatic ring Phenol and addition
of
bromine
water
drop.
(white
layer is cloudy yellow.
2-ol F) Iodoform
2-ol G) Substitution
produced
Observation
Oxidation Ethanol Butan-2-ol 2-methylpropan-
(reaction
was
i.
The solution turns into white solution. When bromine was added, two layers were form. Top layer is cloudy while the bottom layer is clear.
H) Test group Neutral
on Fe
enol (III)
chloride solution
i
The solution turns from colourless to dark blue.
into an aqueous phenol
Questions/Discussions: 1. Select ONE compound from the following pairs of compounds which is more water soluble. Explain your answer. a) Ethanol and hexanol Ans: Ethanol is more soluble in water. Hexanol is not soluble in water. Ethanol consists of two carbon atoms with a single bond between them. So it is easier for a short hydrocarbon chain to bond with water molecules compared to hexanol which is a long hydrocarbon chain. b) Propanol and 1,2,3-propanetriol Ans:
Propanol is more soluble in water. Propanol is an alcohol and polar, and exhibits hydrogen bonding compared to 1,2,3-propanetriol. Water is polar and exhibits hydrogen bonding. The polar natures of the alcohol and water allow the alcohol to be completely miscible in water. 2. Suggest a chemical test(s) to distinguish the following pairs of compounds. Include the reagents, reaction conditions and observations. Write the equation involved. a) 2-butanol and 3-pentanol Ans: To distinguish between 2-butanol and 3-pentanol, solubility test is needed. 2-butanol is easier to bond with water molecule compared to 3-pentanol due to the short hydrocarbon chain of 2-butanol. Reagent: Sodium carbonate solution Reaction condition: Room temperature Observation: 2-butanol form homogenous mixture while 3-pentanol form 2 layer of solution. Equation: R-OH + Na R-O-Na+ + ½ H2 b) Phenol and phenylethanol Ans: To distinguish between phenol and phenylethanol, esterification test is required. Phenol does not form ester by direct reaction with carboxylic acid compared to phenylethanol. Reagent: Carboxylic acid Reaction condition: Room temperature Observation: Phenylethanol form ester directly from the reaction with carboxylic acid. Equation: C6H5OH + R-COOH No reaction c) Phenol and methylphenol Ans: To distinguish between phenol and methylphenol,iodoform test is needed. Methylphenol react quickly with iodine compared to phenol. Reagent: Iodine solution Reaction condition: Room condition Observation: Methylphenol when react with the reagent does not form precipitate. Equation: CH3C6H4OH + 3I- CH3C6HI3OH + 3I 3. Explain the following observations. a) Ethanol is less acidic than phenol. Ans: Phenol is more acidic than ethanol because of the presence of double bond in it. Phenol can remove its hydrogen to make it more stable. Electron density on oxygen atom decreases in comparison to oxygen atom present in alcohols, so phenol can less donate than alcohol. According to Lewis concept of acid and base, which can donate more is more basic and less is acidic.
b) Both phenol and methanol reacts with sodium but only phenol dissolves in aqueous NaOH. Ans: The reason why phenol is more soluble in NaOH than in water is because phenol is slightly acidic. By mixing with NaOH, it causes the phenol to release the H+ to form sodium phenoxide. the reaction between NaOH and phenol is exothermic, and the equilibrium lies far to the right. This makes the sodium phenoxide extra stable. c) 2-methylpropanol does not give yellow precipitate with iodine in NaOH. Ans: A visible precipitate of this compound will form from a sample only when either a methyl ketone, ethanal, ethanol, or a methyl secondary alcohol is present. 2methylpropanol is an primary alcohol, so it does not form precipitate.
d) 1-methylcyclopentanol does not change the purple colour of KMnO4/H+ , ∆ Ans: KMnO4 is pink in a solution without oxidizing reagents. Adding ethanol should change it to a brown solution. If adding ethanol can not change the solution to brown, then its environment is already acidic and will not reduce.
Conclusion: Hydroxyl group are connected to an alkyl carbon are called alcohols. They can be classified into primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols depend on the number of carbon atoms bonded to the carbon with the hydroxyl group. In hydroxyl group, they are alcohol and phenol. This two compound can be distinguish by several tests such as oxdation, solubilty, esterification, Lucas test, iodoform, substitution and test on enol group. Some test produced the same product and reaction while some are not. In conclusion, the reaction of aliphatic alcohols and phenol were investigated.
References: 1. John McMurry, Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry (5th Edition), 2003, pg. 106-126 2. G.L. Patrick, Organic Chemistry, (2nd Edition), 2004.