Static Electricity Detective 3943g
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report l4457
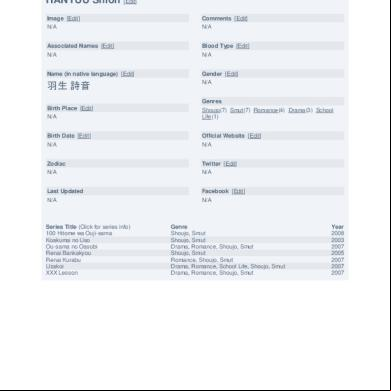
Overview 6h3y3j
& View Static Electricity Detective as PDF for free.
More details h6z72
- Words: 563
- Pages: 3
Static charge detective Section A: Use the following diagram to answer the questions.
1. As you take your clothes out of the dryer, your wool socks are clinging to your silk skirt. What is the charge on the wool socks and on the silk skirt? Charge on socks ____________________________ Charge on skirt ____________________________
3. You use a paper towel to rub off some dirt on a glass window. What is the charge on the glass and on the paper towel?
Charge on window __________________________ Charge on paper towel __________________________
2. You use a plastic comb to comb your hair. What is the charge on your hair and on the comb? Charge on comb ____________________________ Charge on hair ____________________________
4. You rub a balloon along your cat’s back, causing the cat’s fur to stand up. What is the charge on the balloon and on the cat’s fur?
Charge on balloon _____________________________ Charge on cat’s fur _____________________________
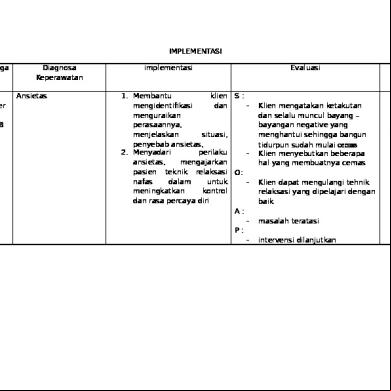
CTION B: 1) Static electricity needs an insulator A balloon is an insulator, this means that electrons are not free to move on its surface. They are stuck in one place.
Balloon and cloth BEFORE being
Balloon and cloth AFTER being
rubbed together
rubbed together
The build-up of negative charges also called _____________ in one place is called static electricity. It is called “static” because it does not move around. The negative charges do not move around because they are on a balloon which is made of rubber. Because of this rubber is known as an _____________. 2) Conductors cannot have static electricity
Metal rod and cloth BEFORE being rubbed together
Metal rod and cloth AFTER being rubbed together
Metal is a _______________, a substance which lets negative charges (also known as ____________) move around freely. Because of this, negative charges do not build up in one place, and _________________ electricity cannot be created. 3)
When there is a difference in negative charges, negative charges will move The negative charges will jump from the places where there are the most number to where there are the least. Complete the following diagrams by adding negative charges (electrons) or a static electricity spark:
a.
b.
c.
d.
Negative charges (or electrons) will always move from where there are the (greatest/fewest) number to where there are the (greatest/fewest) number. If there is a big enough difference and the two objects are close enough together, this jumping may cause a ____________.
4) POINT FOUR: Static electricity can “induce” a charge in neutral object and cause the object to move
1.
2.
Draw the normal spread of negative charges on this piece of tissue (a neutral object)
Draw the build-up of negative charges on this balloon, AFTER it has been rubbed with a cloth
3.
4.
The tissue is now stuck to the balloon. Draw the charges as they now appear.
Draw the same balloon as in stage 1. Draw the charges in the tissue paper so that all the negative charges are far away from the negative charges on the balloon. As they get closer together the tissue is attracted to the balloon
When a neutral object is given a temporary charge, this is called _____________. If the object with a temporary charge is light enough it can be _____________ towards the object that caused the temporary charge.
For each situation illustrated below, will the objects shown attract or repel each other?
1. As you take your clothes out of the dryer, your wool socks are clinging to your silk skirt. What is the charge on the wool socks and on the silk skirt? Charge on socks ____________________________ Charge on skirt ____________________________
3. You use a paper towel to rub off some dirt on a glass window. What is the charge on the glass and on the paper towel?
Charge on window __________________________ Charge on paper towel __________________________
2. You use a plastic comb to comb your hair. What is the charge on your hair and on the comb? Charge on comb ____________________________ Charge on hair ____________________________
4. You rub a balloon along your cat’s back, causing the cat’s fur to stand up. What is the charge on the balloon and on the cat’s fur?
Charge on balloon _____________________________ Charge on cat’s fur _____________________________
CTION B: 1) Static electricity needs an insulator A balloon is an insulator, this means that electrons are not free to move on its surface. They are stuck in one place.
Balloon and cloth BEFORE being
Balloon and cloth AFTER being
rubbed together
rubbed together
The build-up of negative charges also called _____________ in one place is called static electricity. It is called “static” because it does not move around. The negative charges do not move around because they are on a balloon which is made of rubber. Because of this rubber is known as an _____________. 2) Conductors cannot have static electricity
Metal rod and cloth BEFORE being rubbed together
Metal rod and cloth AFTER being rubbed together
Metal is a _______________, a substance which lets negative charges (also known as ____________) move around freely. Because of this, negative charges do not build up in one place, and _________________ electricity cannot be created. 3)
When there is a difference in negative charges, negative charges will move The negative charges will jump from the places where there are the most number to where there are the least. Complete the following diagrams by adding negative charges (electrons) or a static electricity spark:
a.
b.
c.
d.
Negative charges (or electrons) will always move from where there are the (greatest/fewest) number to where there are the (greatest/fewest) number. If there is a big enough difference and the two objects are close enough together, this jumping may cause a ____________.
4) POINT FOUR: Static electricity can “induce” a charge in neutral object and cause the object to move
1.
2.
Draw the normal spread of negative charges on this piece of tissue (a neutral object)
Draw the build-up of negative charges on this balloon, AFTER it has been rubbed with a cloth
3.
4.
The tissue is now stuck to the balloon. Draw the charges as they now appear.
Draw the same balloon as in stage 1. Draw the charges in the tissue paper so that all the negative charges are far away from the negative charges on the balloon. As they get closer together the tissue is attracted to the balloon
When a neutral object is given a temporary charge, this is called _____________. If the object with a temporary charge is light enough it can be _____________ towards the object that caused the temporary charge.
For each situation illustrated below, will the objects shown attract or repel each other?