Laboratory Apparatus And Their Uses 3v2j1f
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report l4457
Overview 6h3y3j
& View Laboratory Apparatus And Their Uses as PDF for free.
More details h6z72
- Words: 391
- Pages: 5
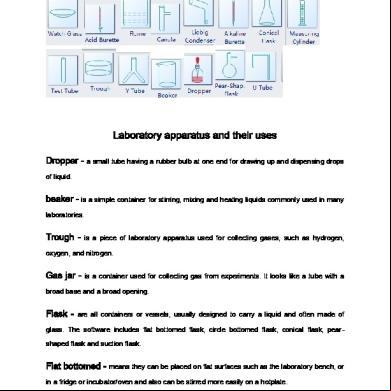
Laboratory apparatus and their uses Dropper -
a small tube having a rubber bulb at one end for drawing up and dispensing drops
of liquid.
beaker - is a simple container for stirring, mixing and heating liquids commonly used in many laboratories.
Trough -
is a piece of laboratory apparatus used for collecting gases, such as hydrogen,
oxygen, and nitrogen.
Gas jar -
is a container used for collecting gas from experiments. It looks like a tube with a
broad base and a broad opening.
Flask -
are all containers or vessels, usually designed to carry a liquid and often made of
glass. The software includes flat bottomed flask, circle bottomed flask, conical flask, pearshaped flask and suction flask.
Flat bottomed - means they can be placed on flat surfaces such as the laboratory bench, or in a fridge or incubator/oven and also can be stirred more easily on a hotplate.
Conical flask - are laboratory vessels that have a wide, flat base and a narrow neck. Test tube -
is usually used to hold the substance in place and that u can observe reactions
taking place.
U tube -
is a glass tube shaped in the form of letter "U" which can be used as a manometer,
and is used in measuring the pressure of liquids.
Pear shape flask -
are made by using very superior and quality raw material
which ensures high durability at its end.
Liebig condenser - are a simple condenser design used to cool and condense hot vapor as part of a distilling apparatus.
Cannula -
is a narrow, flexible plastic tubing used to deliver oxygen through the nostrils of
patients using nasal breathing.
Measuring cylinder - is used to measure the volume solutions, liquids or water. Evaporation dish - is a piece of laboratory glassware used for the evaporation of solids and supernatant fluids, and sometimes to their melting point.
Watch glass -
is a circular, slightly concave piece of glass used in chemistry as a surface to
evaporate a liquid, or as a cover for a beaker.
Acid burette -
is a uniform-bore glass tube with fine gradations and a stopcock at the
bottom, used especially in laboratory procedures for accurate fluid dispensing and measurement.
Alkaline burette -
are simultaneously occupied by the presence of a liquid measuring and
transferring this derailment.
a small tube having a rubber bulb at one end for drawing up and dispensing drops
of liquid.
beaker - is a simple container for stirring, mixing and heating liquids commonly used in many laboratories.
Trough -
is a piece of laboratory apparatus used for collecting gases, such as hydrogen,
oxygen, and nitrogen.
Gas jar -
is a container used for collecting gas from experiments. It looks like a tube with a
broad base and a broad opening.
Flask -
are all containers or vessels, usually designed to carry a liquid and often made of
glass. The software includes flat bottomed flask, circle bottomed flask, conical flask, pearshaped flask and suction flask.
Flat bottomed - means they can be placed on flat surfaces such as the laboratory bench, or in a fridge or incubator/oven and also can be stirred more easily on a hotplate.
Conical flask - are laboratory vessels that have a wide, flat base and a narrow neck. Test tube -
is usually used to hold the substance in place and that u can observe reactions
taking place.
U tube -
is a glass tube shaped in the form of letter "U" which can be used as a manometer,
and is used in measuring the pressure of liquids.
Pear shape flask -
are made by using very superior and quality raw material
which ensures high durability at its end.
Liebig condenser - are a simple condenser design used to cool and condense hot vapor as part of a distilling apparatus.
Cannula -
is a narrow, flexible plastic tubing used to deliver oxygen through the nostrils of
patients using nasal breathing.
Measuring cylinder - is used to measure the volume solutions, liquids or water. Evaporation dish - is a piece of laboratory glassware used for the evaporation of solids and supernatant fluids, and sometimes to their melting point.
Watch glass -
is a circular, slightly concave piece of glass used in chemistry as a surface to
evaporate a liquid, or as a cover for a beaker.
Acid burette -
is a uniform-bore glass tube with fine gradations and a stopcock at the
bottom, used especially in laboratory procedures for accurate fluid dispensing and measurement.
Alkaline burette -
are simultaneously occupied by the presence of a liquid measuring and
transferring this derailment.